Regulatory Challenges and Opportunities in Cryptocurrency: A Comparative Study of India and the U.S.
IAMAI v. RBI and SEC v. Ripple Labs, two cases from different contexts of law,…
Technology DistributionThese tokens function as digital assets that buyers can acquire after they are deposited on the blockchain. The rights package given to the original creator is not included in the aforementioned claim on these assets. Additionally, because the world of digital art is so intricately entwined, imitations of designs and things that are covered by IP rights frequently go unnoticed.
The majority of non-fungible tokens consist of a metadata file that has been encoded using an artwork that may or may not is protected by copyright, or it may even be a work in the public domain. Since anything that can be transformed into a digital format can be used to create an NFT, the original work is only needed in the first step of the process to generate the unique pair of the token identifier and the smart contract address. Therefore, in general, NFTs have very little to do with copyright.
Broadly, NFTs leverage blockchain technology, however apart from the blockchain, a wide range of technologies are incorporated in NFTs. Though during the initial days, the biggest question was on the patent eligibility of NFT technology, in recent years, we have seen a surge in patent filings in this technology space.
Most of these technologies comprise different aspects of NFT like distributed databases, transaction processing, or any improvement in cryptography. These NFT technologies mainly cover different application areas within the NFT environment like management of viewer rights, distribution, a transaction using NFTs, and advanced and improved smart contract related. Taking a deep dive into the patented technologies that explicitly claim NFT rather than innovations in the underlying use of a blockchain as an inventive concept suggests that NFT is gaining traction globally. In the last few years, close to 400 patent families have been published. The patenting trend saw a noteworthy boom in the year 2016 after the first NFT project, Etheria was launched and demonstrated at DEVCON 1 in London.
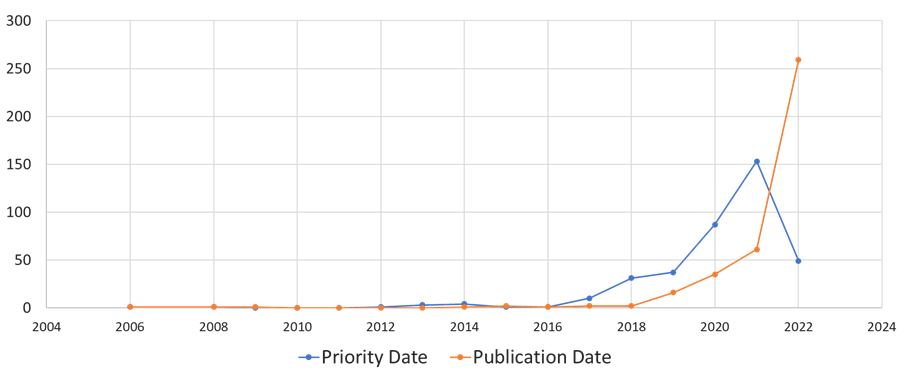
Interestingly, close to 80% of the patents that explicitly claim Nonfungible tokens were published in the year 2022 with the USA being the top choice, followed by Korea. At present, more than 200 research groups and universities are investing their resources to develop technologies that are explicitly meant for NFTs.
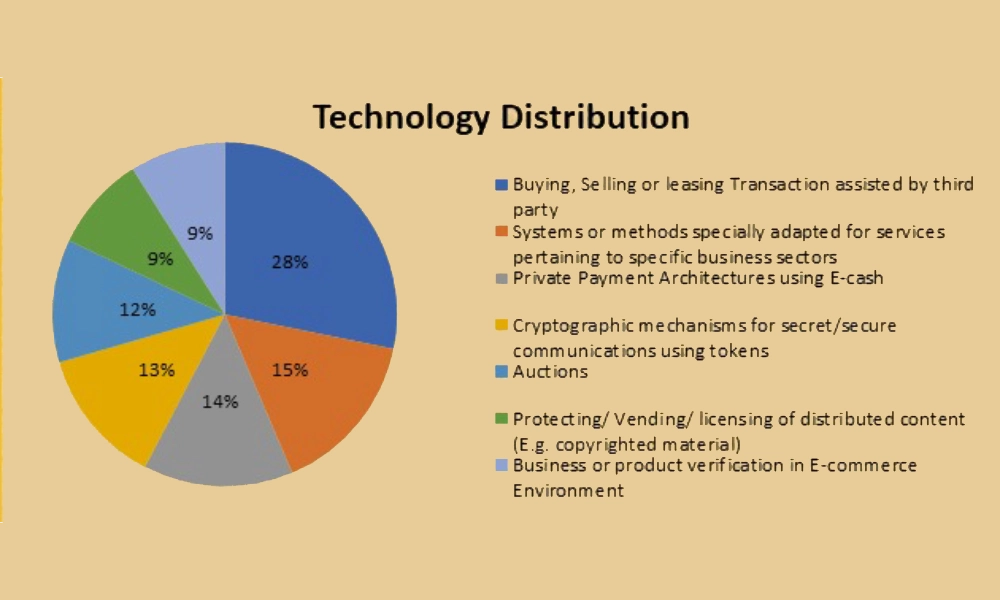
Most of these patented technologies revolve around different aspects of NFT like buying, selling, and leasing transactions assisted by the third party; private payment architecture using E-cash; systems and methods related to protecting, licensing, and distributing protected contents; methods related to verification of digital contents in an e-commerce environment.